GLANET Overview¶
GLANET¶
GLANET is Genomic Loci ANnotation and Enrichment Tool.
Genomic studies identify genomic loci of interest representing genetic variations, transcription factor binding, or histone modification through next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. Interpreting these loci requires evaluating them within the context of known genomic and epigenomic annotations. We present GLANET as a comprehensive annotation and enrichment analysis tool. Input query to GLANET is a set of genomic intervals of any length. GLANET annotates and performs enrichment analysis on these loci with a rich library of genomic elements. GLANET annotation library includes intervals of genomic elements such as:
- regions defined on and in the neighbourhood of coding regions
- ENCODE-derived potential regulatory regions that encompass binding sites for multiple transcription factors, DNaseI hypersensitive sites, modification regions for multiple histones across a wide variety of cell types
- gene sets derived from KEGG pathways
In order to identify the genomic elements enriched in the query set, GLANET implements a sampling-based enrichment test that accounts for systematic biases such as GC content and mappability inherent to NGS technologies. When the input intervals are derived from an NGS experiment, these biases constrain regions of the genome that can contribute to interval generation. Few of the existing tools account for one or both of these biases at coarse-grain level but not at fine-grain level as GLANET does.
We developed GLANET both as an annotation and enrichment tool with several useful built-in analysis capabilities. Users can easily annotate their input intervals with the genomic elements defined in the annotation library and expand the GLANET library by adding user-defined libraries and/or pre-defined gene sets. When the input is a SNP list, users can evaluate whether the SNPs reside in transcription factor binding regions and, if so, whether they are located in the actual transcription factor binding motifs obtainable via either the reference or the SNP allele and whether the variation potentially impacts the binding of TFs, either by enhancing or disrupting binding motifs. GLANET enables joint enrichment analysis for transcription factor binding and KEGG pathways. With this option, users can evaluate whether the input set is enriched concurrently with binding sites of TFs and the genes within a KEGG pathway. This joint enrichment analysis provides a detailed functional interpretation of the input loci.
In order to assess the statistical power and Type-I error control of GLANET, we designed data-driven computational experiments using large collections of ENCODE ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data. These experiments indicated that while GLANET enrichment test often performs conservatively in terms of Type-I error, it has high statistical power.
GLANET can be run using its GUI or on command line.
GLANET Flowchart
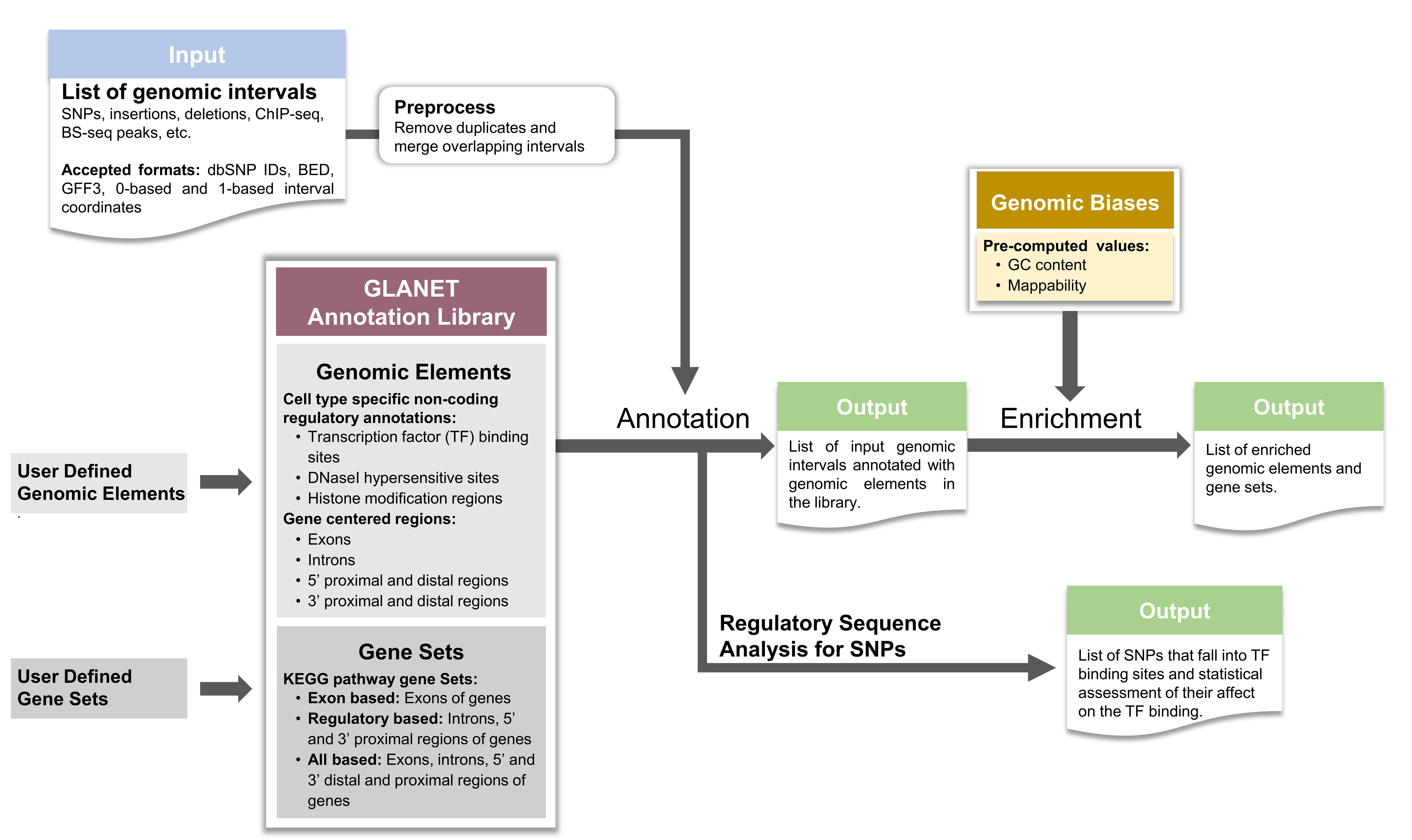
GLANET Features¶
- Users can query SNPs or varying length genomic intervals for annotation and/or enrichment analysis. GLANET supports commonly used input formats such as BED, GFF3, 0-based or 1-based coordinates, and reference SNP (RS) IDs for SNPs.
- GLANET implements a null model that accounts for systematic biases such as mappability and GC content inherent to NGS in order to evaluate whether the input intervals overlap significantly with the genomic elements in the GLANET annotation library.
- GLANET’s sampling-based enrichment analysis also accounts for given interval’s length and the chromosome it is located on in addition to the systematic biases such as mappability and GC content.
- GLANET interprets gene sets in three different ways which are exon-based, regulation-based and all-based manner. Exon-based gene set takes exons of genes, regulation-based takes introns, upstream and downstream proximal regions of genes and lastly all-based takes all the defined regions in exon-based and regulation-based, plus upstream and downstream distal regions of genes of each gene set into account.
- GLANET enables user to load user defined gene sets and/or user defined library and to expand annotation library.
- GLANET provides Regulatory Sequence Analysis using RSAT’s matrix scan web service for all of the annotated TFs when the input consists of SNPs only.
- GLANET has assessed its Type-I error and power by designed data-driven computational experiments on two cell lines, GM12878 and K562, which showed that it has a well-controlled Type-I error rate and high statistical power.
GLANET Output¶
After a successful GLANET execution
Annotation results can be found under
~path/to/GLANET Folder/Output/givenJobName/Annotation/Enrichment results can be found under
~path/to/GLANET Folder/Output/givenJobName/Enrichment/Regulatory Sequence Analysis results can be found under
~path/to/GLANET Folder/Output/givenJobName/RegulatorySequenceAnalysis/GLANET log file (GLANET.log) can be found under the same directory where GLANET.jar is located. If you are running GLANET from the source code, GLANET log file will be created under Glanet project directory.